Juan Alfonzo
Contact Information
Professor at Brown University
Areas of Expertise
- tRNA in mitochondrial bio-genesis and disease
Education
- B.S. Indiana University, 1985
- Ph.D. Indiana University, 1995
- Postdoc, UCLA, 1995-2002
Editing and modification of tRNA: roles in mitochondrial biogenesis and disease
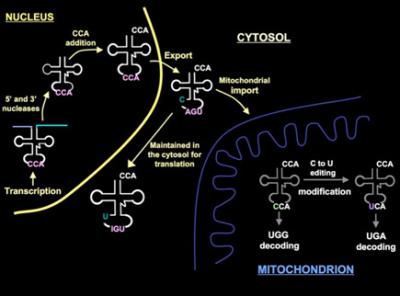
We are interested in RNA processing events that are unique to trypanosomes and could be exploited as targets for the design of therapies against protozoan diseases. To date, the Protozoa are responsible for the infection and death of millions of people worldwide. I am especially interested in two facets of RNA processing in trypanosomes: tRNA editing and tRNA modification.
The mechanism of tRNA editing
RNA editing involves any process by which the information content of a given transcript (mRNA, tRNA, etc.) is changed so that it will differ from that encoded in the genome. RNA editing occurs by a variety of chemically distinct post-transcriptional mechanisms including nucleotide insertion, deletions, base deaminations, and nucleotide exchange (to name a few) and plays an important role in the regulation of gene expression. In trypanosomes, I discovered that the nucleus-encoded tRNATrp undergoes an essential cytosine to uridine editing of the wobble position of the anticodon upon importation into the mitochondrion. Most notable, the deamination of cytosine to uridine at the anticodon allows the decoding of UGA codons as tryptophan. We are interested in the mechanism of tRNA editing and plan to use a genetic and biochemical approach to achieve a complete structure/function analysis of this process in trypanosomes.
The modifications of tRNA and contribution to mitochondrial function
The functional importance of RNA modifications is evident from the large number of phylogenetically conserved modifications that occur in various cellular RNAs. Little is known about the role and extent of RNA modifications in early divergent eukaryotes. In addition, there are increasing numbers of reports linking tRNA modifications with mitochondrial diseases. I plan to use trypanosomes as a model system to study the role that specific tRNA modifications play in mitochondrial function. These studies will be the basis for examining the role site-specific tRNA modifications plays in mitochondrial function. The long-term goal is to utilize the exquisite specificity of these editing and modification enzymes for the long-term applications in gene therapy in humans.
Relevant Publications
Paris Z, Changmai P, Rubio MA, Zikova A, Stuart KD, Alfonzo JD & Lukes J. (2010) The Fe/S cluster assembly protein Isd11 is essential for tRNA thiolation in Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. May 4 [Epub ahead of print].
Phizicky EM & Alfonzo JD. (2010) Do all modifications benefit all tRNAs? FEBS Lett. 584, 265-71.
Wohlgamuth-Benedum JM, Rubio MA, Paris Z, Long S, Poliak P, Lukes J & Alfonzo JD. (2009) Thiolation controls cytoplasmic tRNA stability and acts as a negative determinant for tRNA editing in mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 284, 23947-53.
Alfonzo, JD & Söll D. (2009) Mitochondrial tRNA import - the challenge to understand has just begun. Biol Chem. 390, 717-22.
Rubio, MA, Rinehart J, Krett B, Duvezin-Caubet S, Reichert AS, Söll D & Alfonzo JD (2008) Mammalian mitochondria have the innate ability to import tRNAs by a mechanism distinct from protein import. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 105, 9186-91.
Gaston KW, Rubio MA, Spears JL, Pastar I, Papavasiliou FN & Alfonzo JD (2007) C to U editing at position 32 of the anticodon loop precedes tRNA 5' leader removal in trypanosomatids. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, 6740-9.
Rubio MA, Pastar I, Gaston KW, Ragone FL, Janzen CJ, Cross GA, Papavasiliou FN & Alfonzo JD (2007) An adenosine-to-inosine tRNA-editing enzyme that can perform C-to-U deamination of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 104, 7821-6.
Rubio MA, Ragone FL, Gaston KW, Ibba M & Alfonzo JD. (2006) C to U editing stimulates A to I editing in the anticodon loop of a threonyl tRNA in trypanosomatids. J Biol Chem. 281, 115-20.
Rinehart J, Krett B, Rubio MA, Alfonzo JD & Söll D. (2005) Saccharomyces cerevisiae imports the cytosolic pathway for Gln-tRNA synthesis into the mitochondrion. Genes Dev. 19, 583-92.
